Green ammonia is a new energy vector and a game changer for the hydrogen economy. The CAMPFIRE alliance develops ammonia technologies along the entire value chain for a better tomorrow.
Green ammonia has emerged as a game-changer for the uprising global hydrogen economy. The favourable properties of ammonia overcome many technological hurdles that still exist for hydrogen.
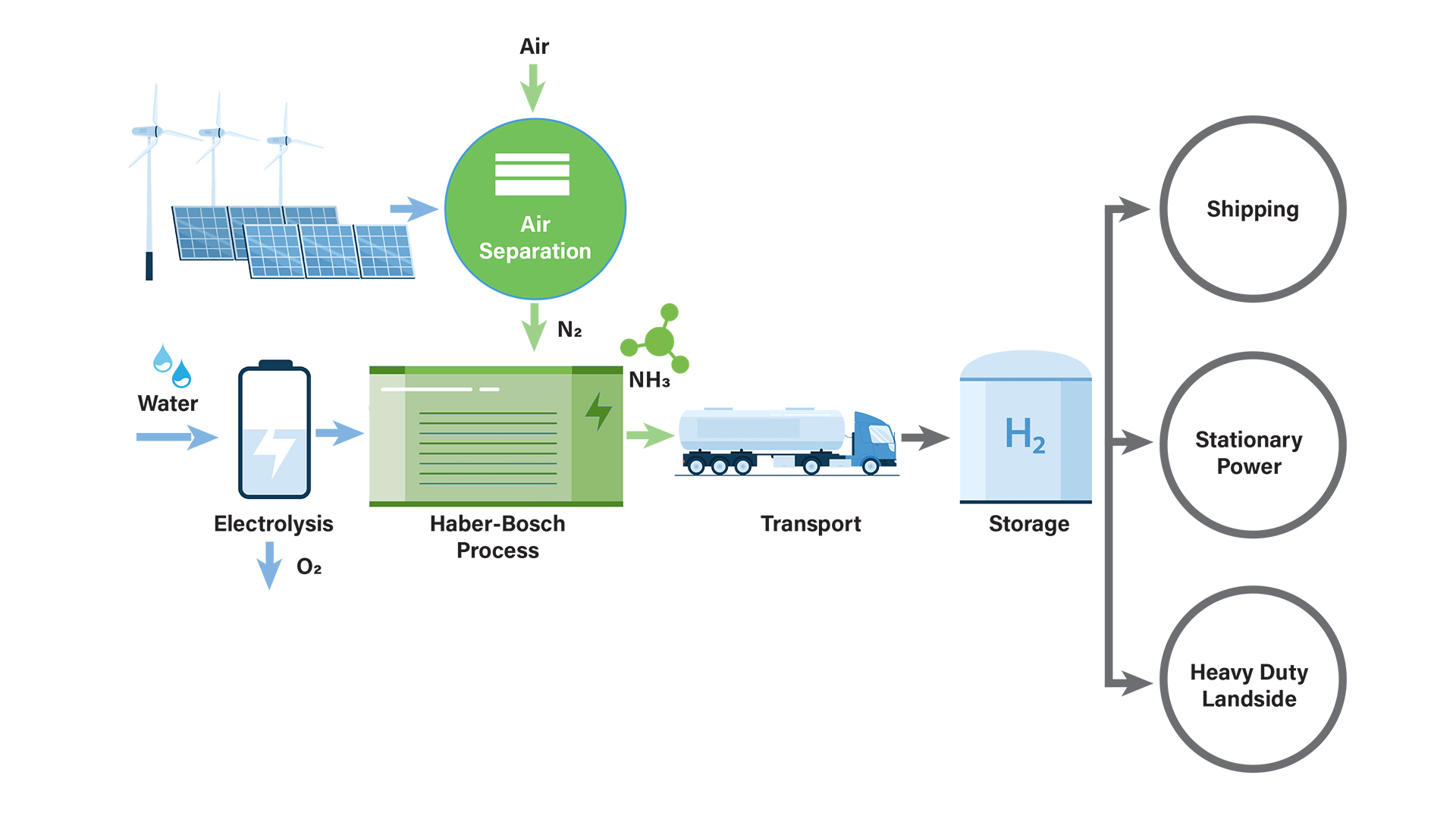
Ammonia is increasingly considered as renewable fuel for shipping, heavy-duty land-based transport, and power generation. With a hydrogen content of around 18%, it offers a great compromise between energy density and production costs and, unlike other synthetic fuels, does not cause any CO2 emissions for the consumer. As a raw material for fertiliser production, around 180 million tonnes of ammonia are already produced annually, and is transported worldwide by pipeline, rail, road, and ship via an established infrastructure. Whilst grey, blue, or turquoise ammonia is produced from natural gas or coal, green ammonia is made by means of renewable energy from atmospheric nitrogen and water.
It is increasingly valued as the major player for the future roll-out of a hydrogen economy, and key to the security of supply in Europe from 2026 onwards. It is truly carbon-free and hydrogen 2.0. Since nitrogen, water, wind and solar are available in abundance, an endless and sustainable supply of ammonia is possible – as fuel and energy storage for a zero-emission future.
The CAMPFIRE alliance
Founded in 2018 as part of the German programme WIR! Wandel durch Innovation in der Region – Regional Development through Innovation of the Federal Ministry of Education and Research, the CAMPFIRE alliance brings together more than 70 partners for the development and implementation of new technologies for the regional production of green ammonia and its use as a marine fuel and energy storage.
The partners are developing innovative products for green ammonia as an energy vector for implementation in renewable energy generation, plant engineering, the chemical industry, shipbuilding and shipping, metal construction, fuel cell and combustion engine producers, lightweight construction, measurement and control technology, and engineering services. They are mostly based in the North-East, but also throughout Germany and Europe. Within the frame of 25 joint projects, technologies are developed for power-to-ammonia and ammonia-to-power.
For small- and medium-scale ammonia production from renewable energy, new catalysts, reactors and plants are developed by the partners ENERTRAG, sunfire, KIT, Gesmex, University of Rostock, INP, and ZBT. New reactor designs involve 3D printed flow guiding elements and shell-and-plate heat exchangers and are coupled with solid oxide or alkaline electrolysers as well as solar thermal technologies for increased efficiency.
Developing ammonia technologies
The focus of the CAMPFIRE alliance is on technologies for direct utilisation of ammonia. Ammonia can be used directly in turbines, fuel cells, and internal combustion engines such as in ship propulsion. To address the poor combustion properties of ammonia, CAMPFIRE partners develop a dual-fuel operation with ammonia and hydrogen as an accelerator. Fuel cells are a class of new marine propulsion technologies.
New Enerday — a SME company in the North-East of Germany developed a solid oxide fuel cell system that can be operated directly with ammonia, offering high efficiencies and currently awaiting its market introduction. In co-operation with partners HanseYachts, autosoft, FVTR, IKEM and ISC as well as research institutes ZBT and INP, an ammonia-cracker-ICE-SOFC marine drive was developed and implemented on board of the yacht ‘Ammonia Sherpa’ in 2023.
The CAMPFIRE cracker-ICE propulsion concept will also be implemented to an inland water way vessel, and ammonia bunkering ship ‘Odin’ in 2026. Currently, a retrofit approach is developed by Tamsen Maritim, Spetrans, DST, DNV, University of Applied Science Stralsund, ISV, KIT, University of Rostock, Liebherr, ABZ Aggregatebau, ELDATA, GaskraftEngineering, FVTR, ZBT, IKEM, and INP for the integration of a cracker-ICE and all required infrastructures.
The propulsion system consists of an ammonia-powered high-speed combustion engine that drives a generator. To improve ignition and efficient conversion of the ammonia in the engine, a cracker is developed by the partner ZBT, which breaks down part of the ammonia into hydrogen and nitrogen, and feeds this mixture to the combustion engine as pilot fuel.
The generator feeds up to 350kWel into a hybrid electric drive train in order to reduce load fluctuations of the cracker-engine unit and to enable distribution to several propeller drives for the shallow-water operation typical of inland waterway vessels. The project also addresses safety, peripheral and tank systems, ship design and training concepts for personnel.
On this base, the partners develop a blueprint for the modification of inland vessels in accordance with project results, the outcome of a parallel economic feasibility study and the procedures required within the existing safety and legal framework. In the future, this blueprint can also be used on seagoing vessels to facilitate the rapid implementation of the new technology for zero-emission shipping and reduce the effects of shipping on climate change.
Partner projects
In the project GreenBalticCruising, CAMPFIRE aims to develop a concept for the Port of Rostock in Northern Germany as a blueprint for a bunker port for green ammonia, ship design and the technological and economic concept for an ammonia-powered cruise ship and a ferry line in the Baltic Sea region. A detailed review of the Baltic Sea countries and suitability of their port structures regarding ammonia was carried out by Port Rostock, DNV and MET to take an important step towards ammonia-based cruise shipping on an international level.
Project partners Carnival Maritim and ZBT conducted a technical evaluation of a new propulsion system for cruise liners consisting of an ammonia cracker and a low-temperature polymer-exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC). The overall objective is to open new economic potential for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in the region by establishing new value chains with equal partnerships in the Baltic Sea Region.
To achieve this goal, partners University of Greifswald, IKEM and INP examined the national strategies for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and the respective climate targets of the neighbouring states, and will identify relevant political, scientific and economic stakeholders. In addition, the legal framework was refined and measures recommended for further development to enable ammonia as a marine fuel in shipping and create new business models through sustainable tourism.
CAMPFIRE partners also develop solutions for stationary energy generation based on combined cracker gas engine CHP for remote off-grid generation. Partners Jenbacher Innio, ZBT, LEC and INP are developing a stationary remote off-grid application in the power range of 1MW.
The development steps include various evaluation steps of critical components of the gas engine, up to the detailed design and implementation of the container CHP plant including the integration of the NH3 cracker and necessary safety equipment. After multi-stage commissioning, various test runs are carried out in which the general mode of operation is tested and operating strategies, including stationary and flexible start/stop operation, are optimised. The focus will be on optimising efficiency and minimising exhaust emissions.
Finally, the results will be used to plan further or comparable plants.
Ammonia refuelling, transport, and storage
CAMPFIRE is also developing ammonia refuelling systems and shoreside and seaside safety systems, including sensor technology for the application in ammonia drives. Based on data on the current supply of fossil fuels, the temporal and spatial demand for green ammonia was forecasted by the partners DST, ISV, Göhler, Elaflex, Dettmer Reederei und Bunker One.
In a first phase of the ramp-up, moderate quantities are initially expected to be supplied to a limited number of ships. For this purpose, a mobile solution in the form of a container module for bunkering the ships, for example by truck, is being developed. As soon as there is a sufficiently large demand for ammonia on the part of the ship fleet, distribution with special bunker ships is advantageous and a corresponding ship design is developed for this purpose. The bunker barge is set to achieve a high safety level in all operating conditions and is flexible in use.
Another project under the CAMPFIRE umbrella focuses on the development of an ammonia-to-hydrogen refuelling station.
A cost-effective fine purification technology for the optimisation of the product gas from an ammonia cracker is key enabling technology developed by partners ZBT, PSL Lasertechnik and Exentis. At its core are CuPd membranes and a novel manufacturing process based on laser welding and 3‑D screen printing for production of the module.
The ultrafine purification system also involves a salt storage tank for ammonia and a high-pressure hydrogen refuelling system. With the determination of the costs for the supply of hydrogen and the derivation of a roadmap for the introduction of ammonia-to-hydrogen refuelling stations in selected regions of Europe.
The future of the ammonia industry
In order to utilise green ammonia as a transport and storage solution for green hydrogen, an efficient infrastructure and a logistics concept geared to the specific framework conditions are required.
Another aim of CAMPFIRE is therefore to develop an economical, sustainable, and ecological logistics and infrastructure concept and to define and investigate associated future scenarios for the transport of green ammonia.
In this context, the needs of industry and transport as well as the already existing and future required sea- and land-based transport facilities, storage, bunkering and transhipment structures are analysed by partners University of Applied Science Wismar, DST, ISC and Dettmer Reederei.
The new concept is based on the evaluation of different scenarios and configurations with regard to the distribution of ammonia in Germany and the associated key figures determined by means of a logistics simulation. The logistics simulation can thus be used to generate essential system knowledge for the construction and coupling of the energy infrastructures. In the future, it can be used to estimate the contribution of ammonia as a transport and storage solution for green hydrogen.
CAMPFIRE partners will continue to develop ammonia technologies as an important key for short-term measures to replace fossil fuels and open economic medium- and long-term avenues for a fast-track decarbonisation of the global energy system. As such, ammonia is an increasingly important global energy carrier for the future economic system. First movers must be supported by strong partnerships across the value chain sharing costs, benefits, and risks.
Please note, this article will also appear in the 18th edition of our quarterly publication.