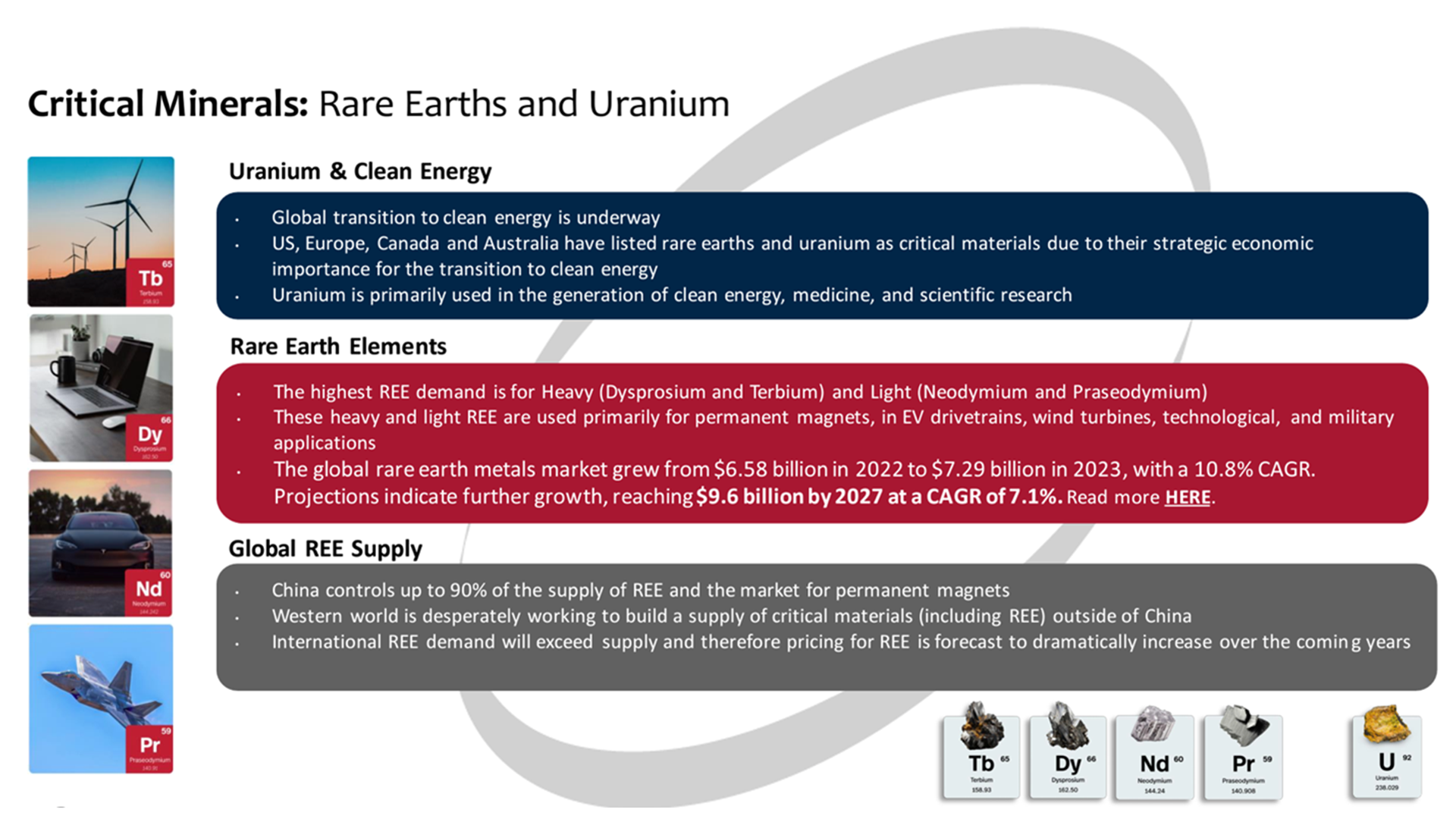
Appia’s portfolio, spanning regions in Canada rich in both REE and uranium, along with the promising PCH Ionic Adsorption Clay REE project in Brazil, has great potential for our clean energy future.
Rare earth elements (REE) remain largely unnoticed in our daily lives. Yet these seventeen minerals, including the priority magnet REE neodymium, praseodymium, dysprosium and terbium, will play a vital role in powering the 21st-century technologies we find in all aspects of our day-to-day lives.
Rare earth bearing minerals are rarely found in the Earth’s crust in significant concentrations, hence their name. REEs possess unique properties that are indispensable in various modern applications, ranging from smartphones and electric vehicles to wind turbines and advanced medical equipment.
Certain rare earth metals, such as terbium and dysprosium, are prized for their heat-adsorbing properties. These magnet REEs play a crucial role in manufacturing powerful magnets vital for electric vehicle motors and wind turbines.
Indeed, these minerals are equally indispensable in our digital world, serving as key components in display screens, compact batteries, and fibre optic cables, driving the technological advancements we benefit from today.
Beyond fuelling technological marvels, rare earth metals are pivotal for achieving a future with renewable energy technologies like solar panels and wind turbines. Their electronic properties optimise the efficiency of these green energy solutions.
The significance of rare earth metals extends beyond practical applications and reaches geopolitical discussions.
With China dominating rare earth metal production, concerns about supply security have arisen globally. Diversifying sources, exploring alternative extraction methods, and fostering international collaboration have become crucial to ensuring a stable and sustainable supply chain.
Uranium’s role in the energy transition
Uranium, often overlooked despite its strategic importance, plays a pivotal role in our world. This is particularly true due to the global renaissance in the nuclear power industry. The IAEA is on record as saying that a ‘doubling’ of nuclear capacity is required by 2050 to achieve climate change goals.
Uranium, derived from uranium oxide (U3O8), is a potent source of clean and efficient energy through controlled nuclear fission, where uranium atoms are split, releasing substantial heat converted into electricity.
Uranium’s significance in achieving climate goals lies in its unparalleled energy density, with a small volume capable of generating millions of times more energy than equivalent amounts of coal or oil. This makes uranium the most efficient fuel for producing massive amounts of electricity, with near-zero CO2 emissions.
In pursuing a clean energy future, uranium will play a crucial role as nations transition away from fossil fuels. As a stable and continuous source of electricity, nuclear power offers an important advantage over weather-dependent solar and wind energy.
The surge in uranium demand and spot pricing reflects the growing acknowledgement of nuclear energy as an essential element in the clean energy mix.
Additionally, the rising demand for nuclear energy, particularly in emerging economies like Asia, is driven by rapid industrialisation and urbanisation, where nuclear power stands out as a reliable and environmentally friendly solution to meet surging energy needs.
Uranium’s remarkable energy properties are key to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future. With the recent upswing in demand and spot pricing reaching a 15-year high in Q4 of 2023, nuclear power is unmistakably gaining traction as a crucial component of our global energy future.
Company overview
Appia Rare Earths & Uranium Corp. (CSE: API / OTCQX: APAAF / FSE: A010) is a publicly traded mining exploration company that is strategically positioning itself to capitalise on the growing demand for critical minerals, including REE and uranium. In advancing this resource development, Appia can play a significant role in helping to meet the increasing input needs for electric vehicles, wind turbines, and advanced electronics.
Appia’s focus on advancing multiple REE and uranium projects is centred around prolific international mining-friendly regions. These mining districts include Goiás State, Brazil, the Athabasca Basin in Saskatchewan and Northern Ontario, Canada. By targeting these strategic locations, Appia aims to maximise the efficiency and success of its exploration efforts.
Demand for critical minerals will continue to rise. With its focus on strategic projects in leading mining jurisdictions, Appia seeks to unlock shareholder value by developing new REE and uranium resources.
Canadian REE and uranium projects
The Athabasca Basin district in Northern Saskatchewan is globally renowned for its rich uranium deposits, making it one of Canada’s most desirable exploration and mining regions. At the heart of Appia’s Canadian operations are five projects strategically positioned in Saskatchewan’s prolific Athabasca Basin:
Alces Lake, one of the company’s flagship projects, is located in northern Saskatchewan. However, its focus is not on uranium but on high-grade REE hosted in monazite.
In addition to Alces Lake, Appia holds four other prospective properties in Northern Saskatchewan. These other projects (Loranger, Eastside, Otherside, and North Wollaston) focus on early-stage uranium exploration.
Beyond the Athabasca Basin, Appia has diversified its Canadian footprint with its Elliot Lake Uranium Project in Ontario, an area globally known for significant historic uranium mining and milling.
Supporting the project’s development, a major Canadian uranium refinery is situated approximately 60km away, near Blind River. This proximity enhances the project’s potential and opens opportunities for synergies with established mining operations.
Elliot Lake, Ontario
Situated in the Algoma District, Ontario, Canada, Appia holds 100% ownership over the Elliot Lake project. This is a substantial land parcel spanning 13,008 hectares (32,143 acres) and strategically positioned between the prominent cities of Sudbury and Sault Ste. Marie.
The geological strength of this expansive property is underscored by the presence of five known mineralisation zones featuring well-established mineralisation of both REE and uranium.
With substantial mineralised zones and defined NI 43-101 resources for both REE and uranium, Elliot Lake is emerging as a promising long-term source for these critical metals. Appia’s CEO, Tom Drivas, framed the potential of Appia’s uranium assets for investors.
He said: “Appia’s uranium portfolio of both past producing and earlier-stage projects positions the company well to participate in the long-term uranium market appreciation. The company holds a large ground position in Elliot Lake with a historical resource (non-NI 43-101 compliant) totalling approximately 199.2 million lbs. of uranium at a grade of 0.76 lbs. U3O8/ton.”
The NI 43-101 Indicated Mineral Resource for the Teasdale Lake Zone stands at 14,435,000 tons with a grade of 0.554 lbs U3O8/ton and 3.30 lbs TREE/ton, resulting in a total of 7,995,000 lbs U3O8 and 47,689,000 lbs TREE. In the Inferred Mineral Resource category, the Teasdale Lake Zone comprises 42,447,000 tons, grading 0.474 lbs U3O8/ton and 3.14 lbs TREE/ton, totaling 20,115,000 lbs U3O8 and 133,175,000 lbs TREE. Additionally, the Inferred Mineral Resource for the Banana Lake Zone is 30,315,000 tons, with a grade of 0.912 lbs U3O8/ton, resulting in a total of 27,638,000 lbs U3O8. The resources are largely unconstrained along strike and down dip. Refer to the NI 43-101 Mineral Resource Estimate page for qualifying notes regarding the Mineral Resource estimates, and individual element grades supporting the reported TREE results.
Click HERE to view the Elliot Lake NI 43-101 Technical Report.
- The historical resource was not estimated in accordance with definitions and practices established for the estimation of Mineral Resources and Mineral Reserves by the Canadian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy (CIM), is not compliant with Canada’s security rule National Instrument 43-101 (NI 43-101), and unreliable for investment decisions;
- Neither Appia nor its Qualified Persons have done sufficient work to classify the historical resource as a current mineral resource under current mineral resource terminology and are not treating the historical resources as current mineral resources; and
- Most historical resources were estimated by mining companies active in the Elliot Lake camp using assumptions, methods and practices accepted at the time and based on corroborative mining experience.
Alces Lake, Saskatchewan
With a vast property covering 38,522 hectares (approximately 95,191 acres), the Alces Lake project offers robust exploration opportunities. Situated where the expansive Canadian Shield extends into northern Saskatchewan, Alces Lake offers both scale potential and high grades of REE.
A total of 34,248.29m has been drilled to date, spread across 316 drill holes. This extensive exploration has uncovered new zones of REE mineralisation, including Jesse and Hinge.
To date, exploration results align with the project’s original geological modelling, indicating substantial potential for expansion of mineralisation and resource development. Appia announced the completion of a NI 43-101 technical report in May 2023 to support further exploration.
Besides Alces Lake, the company already holds four high-potential early-stage uranium projects in the prolific Athabasca Basin area: Loranger, North Wollaston, Eastside and Otherside.
PCH Ionic Adsorption Clay REE, Goiás, Brazil
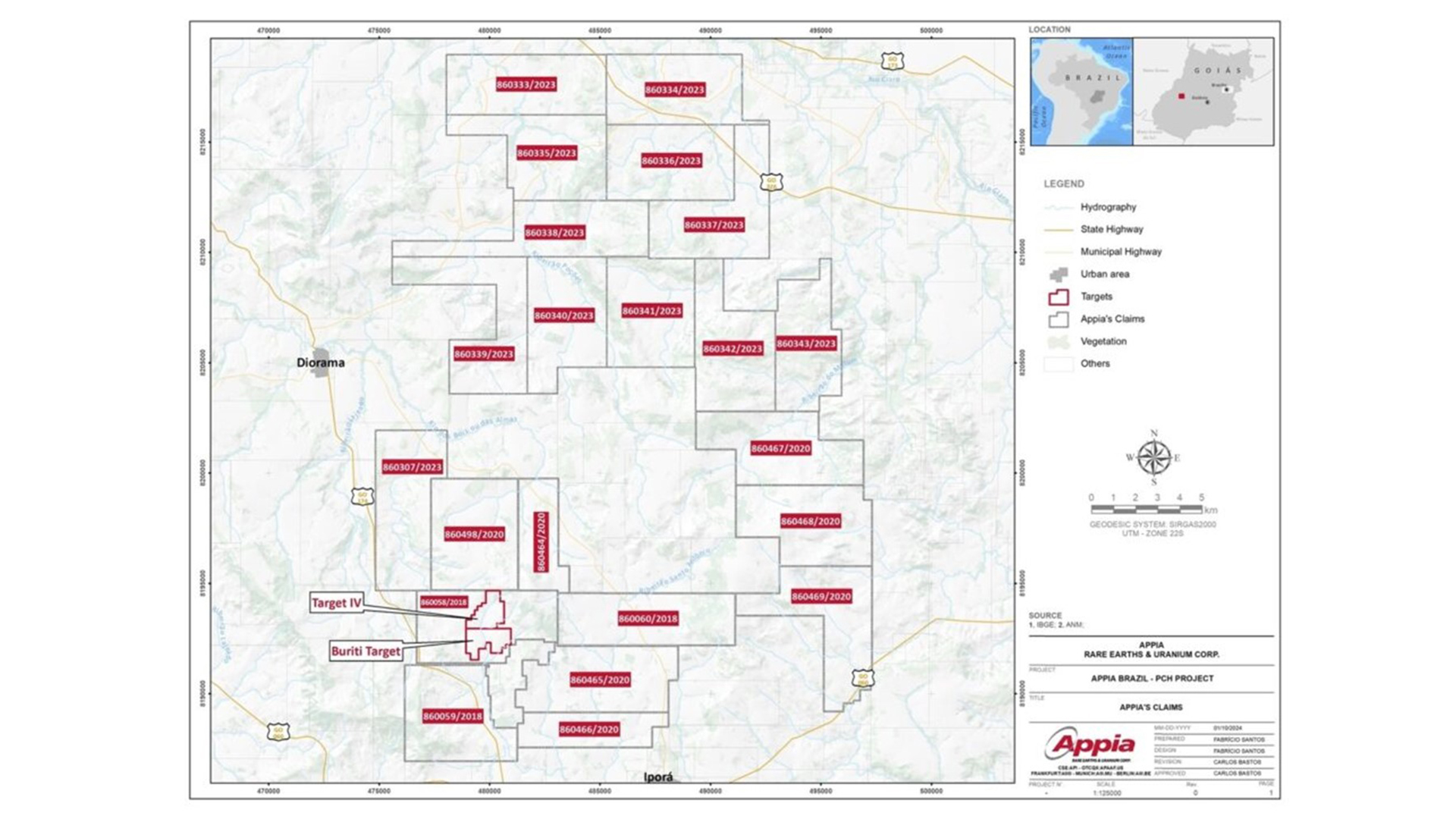
Appia established its international footprint with the acquisition (click HERE) of its PCH Ionic Adsorption Clay (IAC) REE project in Brazil’s Goiás state, where the initial drilling revealed very promising ground-breaking results.
Stephen Burega, President, said: “The expansion of our exploration rights to 40,963.18 hectares (101,222.22 acres) marks a pivotal moment for Appia in Brazil as we build on the momentum achieved through our initial drilling programme at the Target IV and Buriti zones. Our dedicated Brazilian team is eager to explore the untapped potential of the northern corridor, where similar geological and geophysical features have been identified.”
Burega added: “There is huge potential in these new claim blocks as we can draw clear parallels to the favourable geology that hosts the critical rare earth minerals that initially convinced us to enter our agreement on the PCH project. Doubling the size of our overall land package within the prolific alkali province not only reflects our commitment but also strengthens the company’s strategic plans. We aim to develop a series of potential target zones, extending the project focus for the benefit of our valued shareholders.
The headline assay result from this 300-hole drilling programme is a remarkable 24-metre mineralisation zone starting from the surface on drill hole PCH-RC-063, averaging 38,655 ppm or 3.87% Total Rare Earth Oxides (TREO). This includes a higher-grade interval from 10–12m depth, registering an exceptional 92,758 ppm or 9.28% TREO. Click HERE.
PCH Project mineralisation includes significant concentrations of Magnet Rare Earth Oxides, Heavy Rare Earth Oxides, and Light Rare Earth Oxides. This unique discovery extends from the surface and remains open at depth.

These results indicate substantial potential for further expansion of mineralisation at depth, and Appia is currently working with SGS to develop the maiden Mineral Resource Estimate (MRE) on Target IV and Buriti zones of the PCH Project, which will be a crucial part of the NI 43-101 technical report on the PCH project as a whole.
For investors new to REE, Appia’s PCH project discovery is important because mining REE from ionic adsorption clays offers significant benefits, starting with much more efficient exploration.
Unlike traditional REE extraction methods, ionic adsorption clays require less complex and costly processing techniques. This offers additional efficiencies that include streamlined operational procedures, reduced capital costs, and a potentially quicker path to production.
Brazil is a leading mining jurisdiction with a government that has demonstrated a solid commitment to resource development. Government investment and regulatory support play pivotal roles in developing the industry. National strategic initiatives aim to enhance exploration, extraction, and processing capabilities.
Brazil’s national commitment to mining development also extends to many of its state governments. This combined support for project and industry development and its immense resource wealth has made Brazil an increasingly attractive destination for the global mining industry.
With an impressive portfolio spanning regions in Canada rich in both REE and uranium, along with the promising PCH Ionic Adsorption Clay REE project in Brazil, Appia is positioning itself to generate substantial shareholder value in developing meaningful and strategic global assets to help meet the demand for clean energy solutions.
Appia’s future exploration plans run in parallel with what most world experts call for in developing uranium resources as fundamental and crucial in meeting global climate change objectives. Also, seeing the Western world’s need for non-Chinese controlled REE resource development, it has now finally assumed a priority position of strategic importance across all boardrooms and government discussions.
For investors looking to add exposure to these sectors in their portfolio, Appia Rare Earths & Uranium Corp. offers a compelling value proposition.
Please note, this article will also appear in the seventeenth edition of our quarterly publication.








