Researchers from Insilico Medicine have shown how quantum computing can be integrated into the study of living organisms to shed light on biological processes like ageing and disease.
Insilico researchers have presented an image of how combining methods from AI, quantum computing, and the physics of complex systems can help advance new understandings of human health.
In a new paper, the team have also detailed the latest breakthroughs in physics-guided AI.
The research is published in WIREs Computational Molecular Science.
Managing complexity
Although AI has been helpful in processing large, complex biological datasets in order to find new disease pathways and connect ageing and disease at the cellular level, it still faces challenges in applying those insights to complex interactions within the body.
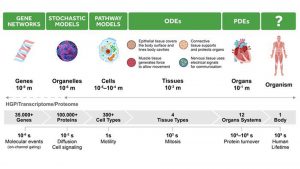
To understand the inner workings of living organisms, scientists need multimodal modelling methods. These models need to manage three key areas of complexity: the complexity of scale, the complexity of the algorithms, and the increasing complexity of datasets.
“While we are not a quantum company, it is important to utilise capabilities to take advantage of the speed provided by the new hybrid computing solutions and hyperscalers,” said co-author Alex Zhavoronkov, PhD, founder and co-CEO of Insilico Medicine.
“As this computing goes mainstream, it may be possible to perform very complex biological simulations and discover personalised interventions with desired properties for a broad range of diseases and age-associated processes.
“We are very happy to see our research centre in the UAE producing valuable insights in this area.”
Computing power is needed to analyse biological data
Biological processes within living systems range from cells to organs to the whole body, with lots of interactions between systems. These processes need to be interpreted on multiple scales simultaneously, and access to biological data has reached unimaginable levels.
The 1000 Genomes Project, for example, is a catalogue of human genetic variation which has identified over nine million single nucleotide variants. As well as this, the UK Biobank contains full sequences from 500,000 genomes of British volunteers.
Massive computing power is needed to analyse and process it.
Quantum computing can interpret biological data
Quantum computing is positioned to augment AI approaches, allowing researchers to interpret across multiple levels of the biological system simultaneously.
Qubits hold values of 0 and 1 simultaneously, having greater computing speed and capability compared to classical bits.
The team note the major advances in quantum computing that are already underway, such as IBM’s debut of both a utility-scale quantum processor and the company’s first modular quantum computer.
Physics-guided AI approach to human biology
The team believe that a physics-guided AI approach will help to increase understanding of human biology. This is a new field that combines physics-based and neural network models.
By combining quantum computing with complex systems, the collective interactions of small-scale elements can be observed at larger levels of reality.









