Kvanttinova’s CEO, Jussi Tuovinen, explains how Finland is transforming its technology ecosystem to become a global leader in chip development.
The vital role of critical technology has been recognised worldwide. Among these critical technologies are semiconductors and microelectronics, or, in short, chips. The European Union declared its stand through the Chips Act in 2022.
Finland excels in specialised manufacturing and integration processes, as well as in complex system-on-chip design. Both have been nurtured through intimate interaction between academic research, applied research and the industry’s efforts to develop the research results into flourishing business.
From our perspective, artificial intelligence (AI) is a major driver for new semiconductor circuits and their power efficiency. Another area for circuits is 6G telecommunication networks for resilient connectivity and sensing communication. Part of this is, for example, antenna beam-steering capacities. Health and medical fields are also important growth areas for us, in addition to defence and space applications. During recent years, newcomer technology has stormed to public awareness: quantum technology for unseen possibilities for computing and sensing. For us, quantum technology has been part of our RDI and commercial portfolio for over three decades.
The Finnish semiconductor industry currently employs roughly 7,000 experts with a combined revenue of €2bn. By 2035, the industry aims to more than triple these numbers. The companies cover the whole industrial value chain and their main customer segments are in telecommunication, automotive, industrial automation, and health technologies.
Kvanttinova: R&D hub for microelectronics and quantum technology
To continue Finnish progress, support growth goals, and build on the existing strong foundation, we present Kvanttinova – an ecosystem for the future of chips and systems, catalysing innovations and having fun while doing it. It is a unique environment offering new product research and development, from design to proof-of-concept validation and, furthermore, pilot lines for small- to mid-volume manufacturing in 200mm and 300mm wafer sizes, i.e. scaling-up from labs to fabs. Innovative circuit design and advanced materials are brought together in Kvanttinova to create novel new devices and products. Application fields for Kvanttinova technologies are, for example, 6G, health and medical, aerospace and defence, as well as AI and quantum computing.
Jussi Tuovinen, CEO of Kvanttinova, said: “Together with our partner network, we are building an even stronger collaboration between research and industry, encouraging significant R&D and design site investments, and even attracting investments in manufacturing sites. A shining ecosystem means prospering businesses and a vast number of new jobs.”
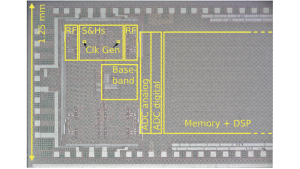
Kvanttinova. State-of-the-art beam forming FD-SOI receiver chip for
sensing applications in collaboration with Aalto University, Tampere
University and Saab is shown in this photo. (IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp.
116375-116383, 2022)
Kvanttinova originates locally from Otaniemi in Espoo, with global impact and outreach.
Growth is a collaborative effort
Kvanttinova is a collaborative effort by VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland, Aalto University, City of Espoo, Enter Espoo, and the Finnish semiconductor industry. It is here to open possibilities for international experts, companies, and investments.
Aalto University is a multifaceted higher education and research powerhouse. VTT has strong expertise in the specialised microelectronics processes and quantum technology. Particularly noteworthy is VTT’s expertise in setting up and leading national and international collaborative projects, bringing together research and industry needs. Espoo’s innovation ecosystem supports the growth of small and large companies by connecting investments and partners to the ecosystem.

Kvanttinova builds on Micronova, an established RDI hub that is well known in the Finnish microelectronics community. The model is already in place with academic and applied research co-located together with the industrial presence. The Micronova cleanroom is used by Aalto University and VTT, which are joined by several companies performing development or even manufacturing operations there.
Espoo innovation community accelerates success
We have our unique recipe and now we are scaling up. Instead of a single cleanroom where companies utilise Aalto University or VTT-owned equipment, we give companies the possibility to have their own cleanrooms, large or small. The cleanrooms are connected internally to the shared-use facilities, thus allowing companies to integrate their operations seamlessly into a larger infrastructure.
Micronova RDI hub has been a vibrant springboard to a host of fascinating, groundbreaking technology companies, such as IQM and SemiQon, and attracted companies to further develop their innovations in the vicinity, such as Dispelix. The multi-user semiconductor piloting environment in Micronova supports the processing of different technologies including micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS) and microoptoelectromechanical systems (MOEMS), quantum devices, radio frequency (RF) components, integrated photonics devices, and 2D materials and post-CMOS processed components.
Espoo’s innovation community in Finland offers globally leading quantum technology and semiconductor expertise, talents, and infrastructure – and will be one of Europe’s significant quantum and semiconductor industry hubs in the future.
IQM Quantum Computers: A global leader in superconducting quantum computers
Hop on the light rail tram in Espoo, and you will be quickly transported to perhaps the world’s most concentrated area of quantum technology expertise. Within a couple of tram stops, you can reach many of Finland’s leading quantum players. One of these is IQM Quantum Computers (IQM) – a global leader in superconducting quantum computers.

IQM was founded in 2018, as it spun out of VTT and Aalto University. Now, the company has its own quantum computer fabrication facility, design, software, and one of the largest quantum engineering teams in the world. IQM designs, builds, and sells on-premises full-stack quantum computers. IQM also provides a cloud platform for customers to access its computers anywhere in the world.
Like many other VTT and Aalto spin-offs, IQM has embraced its strong ties to Espoo’s open innovation community. Together with VTT, IQM launched Finland’s first quantum computer in 2021. In 2023, they unveiled the 20-qubit quantum system. Now, the two are building a 50-qubit computer set to be launched later in 2025.
SemiQon: Helping to make future quantum computers more affordable, scalable and sustainable
Based in Espoo with roots in Micronova, SemiQon is helping to develop silicon-based quantum processors to make future quantum computers more affordable, scalable, and sustainable. The startup spun out of VTT in early 2023.
SemiQon’s technology builds upon decades of development and knowhow from the semiconductor industry, making their silicon processors commercially competitive and well-suited for mass manufacturing. The company believes that the marriage of quantum and semiconductors not only scales up quantum computing effectively but also boosts manufacturing, builds resilience, and supports technological sovereignty. The support from the local quantum and business ecosystem has been pivotal for the company’s success.

Dispelix: Finnish augmented reality (AR) pioneer at the forefront of the fast-evolving waveguide display market
Espoo’s collaborative innovation reality provides the perfect environment for tech development. One of the high-tech developers in this ecosystem is Dispelix, a Finnish augmented reality (AR) pioneer headquartered in Espoo. Dispelix is transforming the future of AR through its transparent display technology, waveguides, which are used as see-through displays in various AR applications. Dispelix display technology can be applied to, for example, near-eye displays for smart glasses and headsets, as well as to head-up displays in vehicles and aviation.
For a high-tech company like Dispelix, Espoo’s innovation ecosystem – with its collaborative working culture, international atmosphere, and facilities like the largest cleanroom in the Nordics at Micronova – offers an open and supportive environment for success.

Dispelix’s pioneering technology is backed by an extensive IP portfolio and skilled personnel of approximately 100 talented employees. Last year, Dispelix celebrated recording its 200th patent in the books for waveguide display technology. Today, this number has grown to over 230, with more than 230 additional patent applications pending. These kinds of milestones are fitting for a science-driven company located in the heart of Espoo’s innovation ecosystem, where the innovation players applied for the sixth most patents in Europe and made 60.5% of all Finnish patent applications last year.
Reinventing the ecosystem – and having fun while doing it
The core of the Kvanttinova infrastructure is the shared-use facility which hosts state-of-the-art equipment for chip development and pilot production on 200mm and 300mm wafers, offering major benefits in improved reliability and repeatability of the processes. The equipment is part of the Chips JU (Joint Undertaking) pilot lines focusing on fully depleted silicon on insulator (FD-SOI) technology (FAMES), heterogeneous system integration and assembly (APECS), sub 2nm system-on-chip (SoC) technology (NanoIC), and photonic integrated circuits (PIXEurope).
The facility offers specific capabilities in material development for such things as ferro- and piezoelectric materials, integration and packaging, superconducting and RF components, and integrated photonics. These piloting lines enable the generation of ideas and their scaling with minimum own capital for the starting entrepreneur.
As important as this fascinating new facility and infrastructure is, we are even more excited to facilitate our community, old and new friends, to meet, to learn and to co-create, leading to growth for us all. A well-known fact is that together we are stronger. Together we can actually have our cake and eat it too. Kvanttinova will grow to a leading semiconductor hub for innovation, providing an environment and support to scale science-based innovations to business.
Kvanttinova welcomes all aspects of microelectronics into a single community. It is a hotspot for encounters and co-creation. We want to achieve a feeling of togetherness among the different actors in our community through working within the RDI hub, attending various events and co-creating arranged, or even random encounters.
Kvanttinova co-operates with educational institutes of all levels to find answers to the common challenge of where to get the skills and talent to achieve the ambitious targets of the semiconductor industry. We’re determined to work hard to promote the field to potential students, starting from the early years to convince the youth of the importance of microelectronics, chips, and systems. By engaging the students already in their studies, we can assure them of a flourishing future and strengthen their understanding of potential careers. Going even deeper, we aim to support the educational institutions in outlining novel educational concepts for up- and re-skilling of existing workforce.
We strongly believe sustainable chip technology leads to vitality and competitiveness of any industrial vertical looking to increase their digitalisation level by integrating chips and systems into their products and offerings. Promoting the benefits while raising awareness of the availability of services for the design and processing of chips will bring new users and customers to services and companies producing chips and systems.
Kvanttinova can assist in finding R&D consortia and funding through its connections. Together with the partners in the Finnish Chips Competence Center (FiCCC), we can bring pilot lines, design centres, and European-level networks of competence closer to all who collaborate with us.
We welcome all interested parties to collaborate with our ecosystem, Kvanttinova.
Please note, this article will also appear in the 21st edition of our quarterly publication.